
The key to start-up of biofilm process in wastewater treatment engineering is science and technology. The deposition of dissolved substances in sewage on the surface of the packing creates conditions for the subsequent colonization of microorganisms and the formation of biofilm, which is the limiting step for the formation of biofilm on the surface of the packing. Strengthening the deposition of dissolved substances in sewage on the surface of the packing is of great significance for speeding up the start-up process of biofilm reactor.
Professor Ren Hongqiang's research group has carried out a systematic exploration in this aspect, and established a rapid quantitative evaluation method for biological affinity of sewage (waste) water treatment fillers based on quartz crystal microbalance monitoring technology. The paper was published in ACS Applied Materials & interfaces (2015, 7 (13): 7222-7230), and two Chinese invention patents (patent numbers: zl201410127046. X and zl201410127048.9) have been granted for the related technical methods. On this basis, the method of chemical and biological enhancement of microbial interface interaction to promote the rapid film formation on the surface of filler has been innovatively designed, and the papers have been published in science of the total environment (2018, 624: 1013-1022) and water research( https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.01.010 )4 invention patents have been applied for (including 1 US patent) and 1 Chinese invention patent has been authorized (Patent No.: zl201611046007.2).
Published online in water on January 8, 2018 The effects of calcium ion and rhamnolipid and their combination on the deposition of dissolved substances in industrial wastewater and simulated wastewater on the surface of typical engineering fillers polystyrene (PS) and polyamide (PA) were systematically investigated, and the applicability of this chemical strengthening method was comprehensively evaluated under different wastewater quality and filler properties. The results show that: the presence of calcium ion can promote the deposition of dissolved substances, and its promotion increases with the increase of concentration. It can promote the deposition of films to be rigid at low concentration, and viscoelastic at high concentration; rhamnolipid can reduce the deposition of substances in low salinity wastewater at low concentration, but it can affect the deposition of substances in high salinity wastewater regardless of its concentration The results show that the deposition of dissolved substances plays a promoting role, but its influence on the properties of the deposited film is more complex; the promoting effect of the combined addition of the two is usually greater than that of the single addition, which indicates that the control of the adhesion and deposition of dissolved substances in wastewater by calcium ion and rhamnolipid is a potential method to accelerate the surface film formation of packing and shorten the start-up time of biofilm reactor.
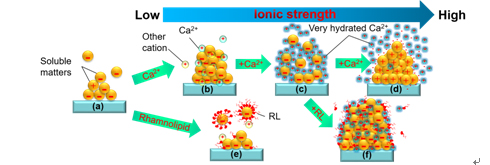
Calcium ion and rhamnolipid enhance the deposition of dissolved substances on the surface of fillers in Wastewater